Digital twins have become a buzzword in recent years, especially in industries like manufacturing and simulation. But what exactly are they and why are they so important? In simple terms, digital twins create a virtual version of something physical. This connection between the real and the digital world helps improve processes, predict outcomes and enhance efficiency. Let’s break down this concept and its applications in manufacturing.
About Digital Twin
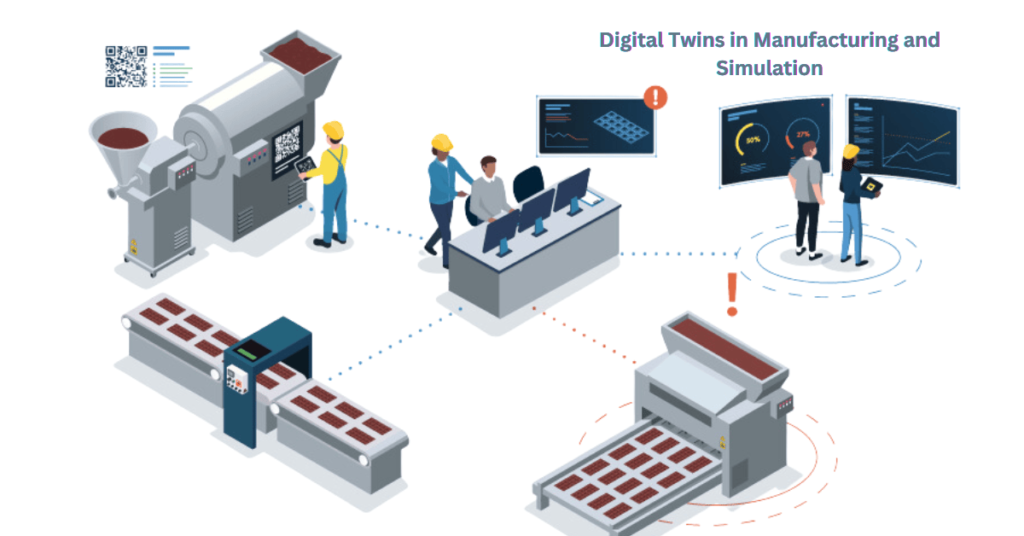
A digital twin is like a high-tech clone of a physical object, process or system. It uses real-time data from sensors and devices to mirror the real world . This virtual model lets businesses monitor , analyze and improve performance without disrupting the physical environment.
Real-Life Examples of Digital Twins
Here are some examples of how digital twins are used in different industries :
- Automotive Industry : Companies like Tesla use digital twins to track car performance, predict maintenance needs and update software remotely.
- Aerospace: NASA uses digital twins to simulate spacecraft performance and identify potential issues before they occur.
- Smart Manufacturing: In factories, digital twins help optimize workflows, reduce downtime and improve efficiency. For instance , Siemens uses them in its smart factory setups.
- Healthcare: Digital twins of medical devices are used to test functionality, spot defects and improve performance before they are put to use.
Popular Digital Twin Software
Creating and using digital twins requires specialized software. Some of the leading tools include :
- Siemens Digital Industries Software: Offers solutions like NX and Teamcenter for building and managing digital twins .
- PTC ThingWorx: A platform focused on integrating IoT technology into digital twin applications.
- Ansys Twin Builder: Known for its advanced simulation capabilities.
- Microsoft Azure Digital Twins: A flexible platform for creating and analyzing digital twins.
- Dassault Systèmes’ 3DEXPERIENCE: A cloud -based tool for collaboration and digital twin development.
How Digital Twins are Used in Manufacturing
Imagine a car factory where a digital twin monitors every part of the production line.
- Detect problems in machines before they break down.
- Test changes to the production process virtually before implementing them in real life.
- Reduce energy usage by identifying inefficiencies .
- Improve product quality by catching defects early.
One well-known example is General Electric (GE) . They use digital twins to monitor jet engines, turbines and manufacturing equipment, ensuring everything runs smoothly.
Types of Digital Twins
There are four main types of digital twins, each serving a specific purpose :
- Component Twins: Focus on individual parts, such as a motor or valve.
- Asset Twins: Represent entire machines or equipment .
- System Twins: Model how multiple machines work together, like an assembly line.
- Process Twins: Cover entire workflows, like how raw materials are turned into finished products.
Digital Twin vs. Simulation: What’s the Difference?
People often confuse digital twins with simulations. While they are related, they aren’t the same:
- Real-Time Updates: Digital twins use live data from sensors, while simulations rely on fixed data or past events.
- Dynamic vs. Static: Digital twins are constantly updated , while simulations are typically one-off exercises.
- Comprehensive View: Digital twins offer a complete picture, while simulations usually focus on specific scenarios.
Think of a digital twin as a smarter, always-on version of a simulation .
How Digital Twins Simulate Reality
Digital twin simulation lets companies test ideas, predict outcomes and improve systems without disrupting operations. For example :
- Factories can test changes to production lines in the digital twin to avoid real-world disruptions.
- Equipment can be monitored for wear and tear in the virtual model , allowing for timely maintenance.
This type of simulation saves time, reduces costs and lowers risks.
Research and Resources on Digital Twins in Manufacturing
Research on digital twins is growing rapidly . Here are some focus areas:
- Artificial Intelligence: Using AI to make digital twins smarter and more predictive.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Combining AR with digital twins for better visualization and interaction.
- Industry 4.0: Exploring how digital twins can transform modern manufacturing through automation and data-driven decision-making.
Tips for Presenting Digital Twins in Manufacturing (PPT)
If you’re creating a presentation on digital twins, keep it simple and focused. Include:
- What They Are: A clear definition and overview.
- Real-World Examples: Showcase how companies are using them.
- Key Technologies: Discuss IoT, software platforms and AI integration.
- Benefits: Highlight cost savings , efficiency and improved quality.
- Future Trends: Mention ongoing research and advancements.
Adding visuals, case studies and diagrams can make your presentation more engaging and easier to understand.
Final Thoughts
Digital twins are changing the game in manufacturing by offering a virtual way to monitor, simulate and optimize operations . From improving product quality to predicting maintenance needs, the potential applications are endless. As technology advances , digital twins will continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of manufacturing and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What is a digital twin?
A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical object, system, or process. It uses real-time data from sensors and devices to mirror the real world, enabling monitoring, analysis, and optimization without disrupting physical operations.
How are digital twins used in real life?
Digital twins are used in many industries, including:
Automotive: Tesla uses them to monitor car performance and enable remote updates.
Aerospace: NASA uses them to simulate spacecraft performance.
Manufacturing: Siemens employs them to optimize smart factory workflows.
Healthcare: Digital twins test and improve medical devices.What software is used to create digital twins?
Popular software platforms for digital twins include:
Siemens Digital Industries Software
PTC ThingWorx
Ansys Twin Builder
Microsoft Azure Digital Twins
Dassault Systèmes’ 3DEXPERIENCE
These tools help integrate IoT data, simulate scenarios, and analyze performance.What is the difference between a digital twin and a simulation?
Digital Twin: Uses real-time data from sensors and is constantly updated. It provides a complete, dynamic view of a system.
Simulation: Relies on historical or fixed data and is typically a one-off exercise. It focuses on specific scenarios rather than providing a holistic view.What research is being done on digital twins in manufacturing?
Current research focuses on:
Using AI to make digital twins smarter and more predictive.
Integrating augmented reality (AR) with digital twins for better visualization.
Exploring how digital twins fit into Industry 4.0, with emphasis on automation and data-driven decision-making.